http://elpais.com
スペインの財政危機による信用不安から、スペインの国債の金利は異常な高値に上昇し、銀行危機と共に、スペインの国家予算の資金調達は非常な困難に陥る(2012年8月には国債の満期返済ができなくなって破綻するだろうけれど??)
Las dudas enredan la ruta del Tesoro
El alto coste de las emisiones y la crisis bancaria ponen difícil la financiación a España
Archivado en:
- Crisis económica
- Bonos Tesoro
- Tesoro Público
- Recesión económica
- Deuda pública
- Fondos inversión
- Coyuntura económica
- Financiación déficit
- Crisis financiera
- Déficit público
- Finanzas públicas
- Mercados financieros
- Finanzas
- Economía
Fuente: Secretaría General del Tesoro y Política Financiera, Bloomberg. / EL PAÍS
Doubts Treasury tangled path
The high cost of emissions and the banking crisis put the financing difficult to Spain
Amanda Madrid Mars 3 JUN 2012 - 00:00 CET
The high cost of emissions and the banking crisis put the financing difficult to Spain
Amanda Madrid Mars 3 JUN 2012 - 00:00 CET
"The chances of disaster are few, true, but if I told you I carry in my car to the airport with only 10% chance of an accident, would you come with me or take a taxi? That happens with Spain, with the huge amounts of money at stake, our investors do not want to risk. " So spoke a few days ago after visiting Madrid an executive of one of the largest investment firms in the world to explain why the market is so difficult for the fourth European economy.
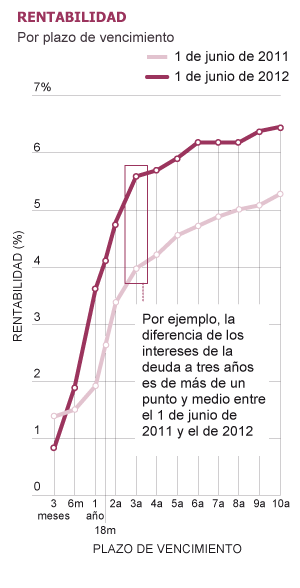
The Treasury has to pay more and more to borrow money, for each bond and letter issued as a result of the growing doubts about the ability to revive the economy and the solvency of banks. And that complicates their roadmap. The risk premium, which is the premium required of Spanish bonds compared to the reliable Germans, marking the European benchmark, closed on Friday, its worst week of the stage euro came to play the 547 basis points (or 5, 4 percentage points) and reached 6.7% interest.
THE COUNTRY
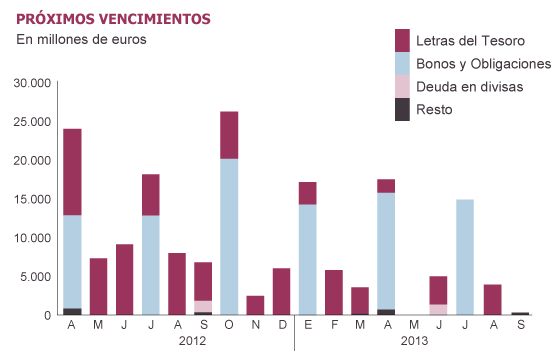
The Treasury is ahead of schedule and are just 3,000 million net issuance of debt outstanding (ie, volume of new debt, net of depreciation) explain to the Ministry of Economy. But the numbers get fat if you put the focus on the total gross issuance, the total amount that the body should still ask to investors. Spain had planned for this year gross issuance of 86,000 million in notes and bonds (maturing in the medium and long term) and 100,000 million in short-term letters. So far has already covered 56.2% of bonds under (48,313,000) and 34% of the letters (34,000 million), although in this case the depreciation equal to the emissions and the net effect is zero. Now it put the rest and the cost continues to grow, not only for the 10-year bonds, which were the first to suffer the sovereign debt crisis, but in securities maturing in the shorter term.
Titles a year and are exchanged on the secondary market (where investors buy and sell bonds and notes already issued) to 3.5% when they were just a year ago at 2.5%. And the titles to five years are about 6%, against 4.5% a year. What happens in this cove secondary market after the auction. And at last, the Treasury paid the 5% bonds with the same period of life.
Meanwhile, Germany is financed almost free: in May last year managed to sell 4,560 million in bonds to two years with a minimum interest of 0.07%. Few data are so illustrative of this two-speed Europe, panic running to take refuge in the winter quarters. Held auctions for months with negative interest, ie the German Treasury came to charge for borrowing money.
This stems from the cost of financing is particularly troubling when the banking crisis has entered its most critical phase. The financial industry will need more public money. The rescue of Bankia cost an additional € 19,000 million of public money and helps the rest of the sector required to meet new requirements for recapitalization are unknown. If the standard applied in Bankia hard to sanitize the surfeit of real estate credit risk is extrapolated to the rest of the system, analysts calculated a requirement of capital of 50,000 million and more entities will require public support to fund it.
more informationThe interest you pay Spain for finance rises 1.3 percentage points in 2011Communities face this year maturities 35.782 millionThe risk premium is triggered by the rejection of the plan on Bankia ECB
The Government seeks to avoid market and the bank bailout fund (FROB) or the Treasury does not have to borrow money. Battle for the European rescue fund, through legislative change, to inject money directly to European entities that request without going through the states. It would be the way to rescue the banking avoiding the stigma of asking for money from Europe from Spain.
The Government has continued to polish the smooth running of the calendar (in five months has placed more than half of debt announced), allowing you time frame: it has a cushion of 44,000 million euros deposited in the Bank of Spain. The strategy, given the hostile market through the brake at the next auction, ie least amount of debt placed so as not to pay interest too high. "It will follow a very prudent strategy" merely identify sources of Economy. On Thursday they have a new test on the market, a bond auction. Ahead are more than 80,000 million to repay debt until the end of the year, with two important deadlines, 18,625,000 in June and 27,365 in October.
The Treasury has to pay more and more to borrow money, for each bond and letter issued as a result of the growing doubts about the ability to revive the economy and the solvency of banks. And that complicates their roadmap. The risk premium, which is the premium required of Spanish bonds compared to the reliable Germans, marking the European benchmark, closed on Friday, its worst week of the stage euro came to play the 547 basis points (or 5, 4 percentage points) and reached 6.7% interest.
THE COUNTRY
The Treasury is ahead of schedule and are just 3,000 million net issuance of debt outstanding (ie, volume of new debt, net of depreciation) explain to the Ministry of Economy. But the numbers get fat if you put the focus on the total gross issuance, the total amount that the body should still ask to investors. Spain had planned for this year gross issuance of 86,000 million in notes and bonds (maturing in the medium and long term) and 100,000 million in short-term letters. So far has already covered 56.2% of bonds under (48,313,000) and 34% of the letters (34,000 million), although in this case the depreciation equal to the emissions and the net effect is zero. Now it put the rest and the cost continues to grow, not only for the 10-year bonds, which were the first to suffer the sovereign debt crisis, but in securities maturing in the shorter term.
Titles a year and are exchanged on the secondary market (where investors buy and sell bonds and notes already issued) to 3.5% when they were just a year ago at 2.5%. And the titles to five years are about 6%, against 4.5% a year. What happens in this cove secondary market after the auction. And at last, the Treasury paid the 5% bonds with the same period of life.
Meanwhile, Germany is financed almost free: in May last year managed to sell 4,560 million in bonds to two years with a minimum interest of 0.07%. Few data are so illustrative of this two-speed Europe, panic running to take refuge in the winter quarters. Held auctions for months with negative interest, ie the German Treasury came to charge for borrowing money.
This stems from the cost of financing is particularly troubling when the banking crisis has entered its most critical phase. The financial industry will need more public money. The rescue of Bankia cost an additional € 19,000 million of public money and helps the rest of the sector required to meet new requirements for recapitalization are unknown. If the standard applied in Bankia hard to sanitize the surfeit of real estate credit risk is extrapolated to the rest of the system, analysts calculated a requirement of capital of 50,000 million and more entities will require public support to fund it.
more informationThe interest you pay Spain for finance rises 1.3 percentage points in 2011Communities face this year maturities 35.782 millionThe risk premium is triggered by the rejection of the plan on Bankia ECB
The Government seeks to avoid market and the bank bailout fund (FROB) or the Treasury does not have to borrow money. Battle for the European rescue fund, through legislative change, to inject money directly to European entities that request without going through the states. It would be the way to rescue the banking avoiding the stigma of asking for money from Europe from Spain.
The Government has continued to polish the smooth running of the calendar (in five months has placed more than half of debt announced), allowing you time frame: it has a cushion of 44,000 million euros deposited in the Bank of Spain. The strategy, given the hostile market through the brake at the next auction, ie least amount of debt placed so as not to pay interest too high. "It will follow a very prudent strategy" merely identify sources of Economy. On Thursday they have a new test on the market, a bond auction. Ahead are more than 80,000 million to repay debt until the end of the year, with two important deadlines, 18,625,000 in June and 27,365 in October.
0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿